Definition
There are two types: CRPS Type I and CRPS Type II. Type I has no definitive nerve injury, where Type II does. Treatment is similar for both types. CRPS symptoms can be temporary and eventually resolve, but most are long term(chronic). If untreated, the condition can be devastate one’s quality of life.
Symptoms
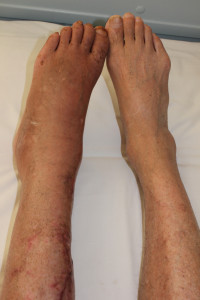
The primary symptom is pain. Neuropathic, or nerve, pain is typically described as “burning” or “pins and needles”. It typically affects a single limb, but can sometimes spread to the opposite limb. Most patients suffer from allodynia, which is hypersensitivity or pain to usually non-painful normal or light touch. Other common features are temperature/color changes and swelling. Some patients may experience abnormal hair or nail growth in the affected area.
Causes
CRPS is most commonly triggered by trauma or injury. There is no way to predict who will develop CRPS as a response to a trauma. Common triggers can include fractures, sprain/strains, soft tissue injury (burns, cuts, bruises), limb immobilization (casting), surgery, and minor medical procedures such as needle sticks.
Diagnosis
There is no diagnostic test to confirm CRPS. The condition is diagnosed by clinical evaluation. It is important to rule out other conditions that may present similarly. Electromyography (EMG/NCS) can be useful in the case of CRPS Type II. MRI and triple phase bone scan may also aid in the diagnosis.
Treatment
Physical Therapy can be helpful in maintaining good movement and range of motion of the affected area, as well as maintaining good blood flow, flexibility and strength. Psychotherapy may help people who develop depression, anxiety or PTSD (post-traumatic stress disorder). These conditions may heighten the perception of pain and make the pain more difficult to treat.
Medications are typically focused on those that treat neuropathic (nerve injury) pain. There are many different types of medications available to treat pain and should be done with a provider specialized in treating CRPS type pain.
Sympathetic nerve blocks are frequently done by interventional pain specialists and may provide temporary relief. Local anesthetic is injected along a group of sympathetic nerves next to the spine to block the nerve hyperactivity and improve blood flow.
Spinal cord stimulators are typically effective for any neuropathic pain condition, including CRPS. A device is surgically implanted along the spinal cord to provide electrical stimulation and reduce pain, improve function, and often reduce the need for oral pain medications.
Other neurostimulators. If a localized area or single nerve is identified to be the culprit, a patient may benefit from a peripheral nerve stimulator or DRG stimulator.
For refractory cases, other treatments are available. Visit: Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Fact Sheet for more information.

